Sunscreen and the Skin Barrier: What You Need to Know
Discover how sunscreen and the skin barrier work together. Learn why daily use, especially with ceramides, is crucial for skin health and UV protection.
Alright, let's talk about something super important: your skin. It's like your body's personal bodyguard, keeping the bad stuff out and the good stuff in. But, like any good bodyguard, it needs backup sometimes.
That's where sunscreen and the skin barrier come into play. I've been in the skincare game for a while, and trust me, understanding this is a game-changer. Sunscreen isn't just about avoiding a nasty sunburn; it's about keeping your skin's defense system strong.
👉Let's dive in, and I'll explain why this is so crucial, in a way that even a 12-year-old can get it.
Key Takeaways: Sunscreen and the Skin Barrier
- Sunscreen and the skin barrier are like best friends; one protects the other.
- UV rays from the sun are like the bad guys, trying to mess up your skin.
- Ceramides in sunscreens are like the secret weapon that boosts your skin's defense.
- Using the right sunscreen can keep your skin hydrated and happy.
- Not all sunscreens are created equal; some are better for your skin barrier than others.
- Regular use of sunscreen helps prevent long-term damage and keeps your skin looking young.
Why Your Skin Barrier is a Big Deal
Think of your skin barrier as a brick wall. It's made up of cells (the bricks) and lipids (the mortar) that hold everything together. This wall keeps moisture in and irritants out.
When it's strong, your skin is healthy and glowing. When it's weak, you get dryness, irritation, and all sorts of problems. I remember once, I skipped sunscreen on a beach trip – big mistake. My skin barrier got wrecked, and it took weeks to recover.
😐Lesson learned: protect your barrier!
- Skin barrier is crucial for keeping skin healthy.
- A strong barrier prevents dryness and irritation.
- Damage to the barrier can lead to various skin issues.
- Maintaining a healthy barrier is key to radiant skin.
The Sun's Sneaky Attack: UV Rays
The sun is awesome, but it's also a bit of a bully. It sends out these invisible rays called UV rays, which can do a number on your skin. These rays cause oxidative damage, which is a fancy way of saying they mess up your skin cells.
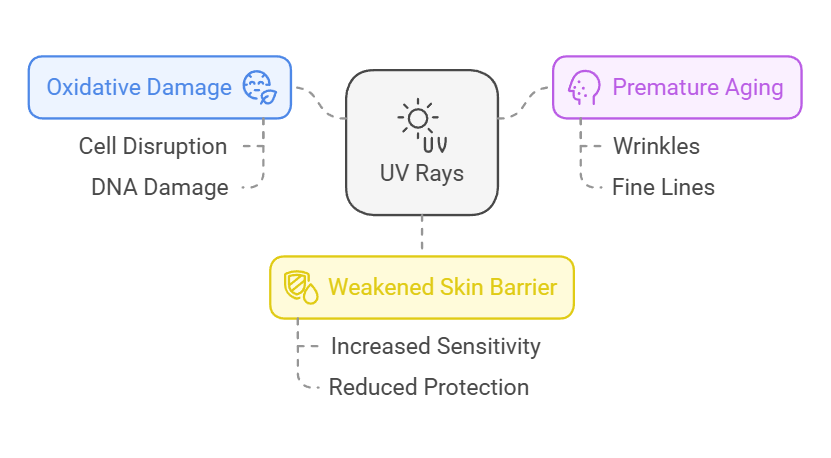
This can lead to premature aging, wrinkles, and even skin cancer. Plus, UV rays weaken your skin barrier, making it harder for your skin to do its job. It's like poking holes in that brick wall we talked about.
- UV rays cause oxidative damage to skin cells.
- They can lead to premature aging and wrinkles.
- UV exposure weakens the skin barrier.
- Protecting against UV rays is essential for skin health.
Sunscreen: Your Skin's Best Friend
This is where sunscreen comes in. It's like a shield that blocks those harmful UV rays. But not just any sunscreen will do. You want one that not only protects you from the sun but also supports your skin barrier.
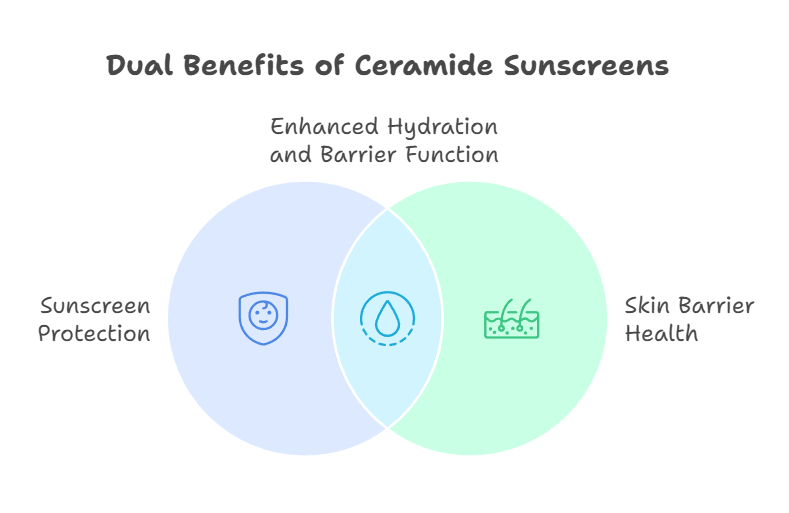
That's where ceramides come in. These are like the super-glue that helps repair and strengthen your skin barrier. Using a ceramide-containing sunscreen is like giving your skin a double dose of protection. I always tell my clients, "It's not just about blocking the sun; it's about building up your skin's defenses."
| Sunscreen Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Sunscreen | Blocks UV rays, prevents sunburn |
| Ceramide-Containing Sunscreen | Blocks UV rays, strengthens skin barrier, hydrates skin |
Ceramides: The Secret Weapon in Sunscreen and the Skin Barrier
Ceramides are a type of lipid that makes up about 50% of your skin barrier. They're essential for keeping your skin hydrated and resilient. When you use a sunscreen with ceramides, you're not just protecting your skin from the sun; you're also replenishing these vital lipids.
Studies have shown that ceramide-containing sunscreens can increase skin hydration by over 20% and reduce transepidermal water loss (TEWL) – that's a fancy term for how much water your skin loses. Less water loss means a stronger, healthier barrier. For more on how ceramides can help, check out Ceramides for Skin Barrier Health.
- Ceramides make up 50% of the skin barrier.
- They are crucial for skin hydration.
- Ceramide-containing sunscreens enhance barrier function.
- They reduce transepidermal water loss.
The Science: How Sunscreen Improves Skin Hydration
Let's get a bit nerdy for a second. A study published in 2023 showed that using a ceramide-containing sunscreen for four weeks led to a 21.96% increase in skin hydration. That's huge! It means your skin is better at holding onto water, which is essential for a healthy barrier.
Plus, these sunscreens reduced skin redness and inflammation. So, not only are you protecting your skin from the sun, but you're also making it healthier and more resilient. "It's like giving your skin a drink of water and a protective shield at the same time," as one dermatologist put it.
A study found that ceramide-containing sunscreens significantly improve skin hydration and barrier function.
| Parameter | Improvement After 4 Weeks |
|---|---|
| Skin Hydration | 21.96% increase |
| TEWL | 22.96% reduction |
| Skin Redness | 11.89% decrease |
Sunscreen and Inflammation: Keeping Your Skin Calm
Inflammation is another big issue for your skin. It can cause redness, irritation, and even acne. Sunscreens, especially those with ceramides, have anti-inflammatory effects. They help calm your skin and reduce redness. This is super important because chronic inflammation can weaken your skin barrier over time.
By using the right sunscreen, you're not just protecting your skin from the sun; you're also keeping it calm and happy. If you're dealing with sensitive skin, you might want to read up on Skin Barrier Repair for Sensitive Skin.
- Sunscreens reduce skin inflammation.
- Ceramide-containing sunscreens have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Reducing inflammation helps maintain a healthy skin barrier.
- Chronic inflammation can weaken the skin barrier.
Protecting Your Skin from UV-Induced Damage
Remember that UV damage we talked about?
Well, ceramide-containing sunscreens are like the ultimate defense against it. They protect your skin barrier from the damage caused by UV exposure, keeping it functioning like it should.
One study simulated two hours of sun exposure and found that skin treated with ceramide products maintained its barrier function just like unexposed skin. That's incredible! It means you can enjoy the sun without wrecking your skin. "Think of it as a force field for your skin," I often say.
- Ceramide-containing sunscreens protect against UV-induced damage.
- They maintain the skin barrier function similar to unexposed skin.
- Using these products helps prevent long-term damage.
- They are essential for maintaining healthy skin in sunny conditions.
Choosing the Right Sunscreen: Not All Are Created Equal
Now, you might be thinking, "Okay, I get it. Sunscreen is important. But which one should I choose?"
That's a great question.
Not all sunscreens are created equal. You want to look for one that's broad-spectrum, meaning it protects against both UVA and UVB rays. And, of course, you want it to contain ceramides. These ingredients are like the dynamic duo of skincare.
They protect and repair at the same time. I always recommend doing a patch test first to make sure your skin doesn't react to a new product.
For tips on choosing the right moisturizer, which is equally important, check out Best Moisturizers for Skin Barrier Repair.
New research highlights the benefits of ceramides in protecting the skin barrier from UV exposure.
- Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen.
- Look for ceramides in the ingredients.
- Do a patch test before using a new product.
- Combine sunscreen with a good moisturizer for best results.
Daily Use: Making Sunscreen and the Skin Barrier Part of Your Routine
Here's the thing: using sunscreen shouldn't be a once-in-a-while thing. It needs to be a daily habit, just like brushing your teeth. Even on cloudy days, those sneaky UV rays can still get through. Make it a part of your morning routine. Apply it after your moisturizer but before your makeup.
And don't forget to reapply every two hours, especially if you're swimming or sweating. Consistency is key when it comes to skincare. Trust me, your future self will thank you.
For more on establishing a good routine, read Restore Your Skin Barrier: A Simple and Effective Guide.
- Use sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days.
- Apply after moisturizer and before makeup.
- Reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Make sunscreen a consistent part of your skincare routine.
Conclusion
Alright, let's wrap this up. Sunscreen and the skin barrier are a match made in heaven. Using a ceramide-containing sunscreen not only protects you from the sun's harmful rays but also strengthens your skin's natural defenses. It's like giving your skin a superpower.
Remember, your skin is your body's first line of defense, and taking care of it should be a top priority. So, make sunscreen a daily habit, choose the right products, and your skin will thank you.
Stay consistent, stay protected, and keep that skin barrier strong. You've got this!
Frequently Asked Questions: Sunscreen and the Skin Barrier - What You Need to Know
Why is the Skin Barrier So Important, and How Does Sunscreen Help?
Your skin barrier is your first line of defense against the outside world, including the sun's harmful UV radiation. It's like the walls of a fortress, keeping the good stuff in (like moisture) and the bad stuff out (like UV rays, pollutants, and irritants).
Sunscreen acts as a shield, protecting your skin barrier from UV damage that can lead to dryness, inflammation, premature aging, and even skin cancer. The Skin Cancer Foundation emphasizes the importance of daily sunscreen use for skin health.
What's the Difference Between UVA and UVB Rays, and Why Should I Care?
UVA rays are the "aging" rays that penetrate deep into the skin, damaging collagen and elastin fibers, leading to wrinkles and premature aging. UVB rays are the "burning" rays that primarily affect the skin's surface, causing sunburn.
Both types of rays can damage the skin barrier and increase the risk of skin cancer. A broad-spectrum sunscreen, as recommended by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
How Do Ceramides in Sunscreens Help Strengthen the Skin Barrier?
Ceramides are essential lipids (fats) that make up a significant portion of the skin barrier's structure. They're like the mortar that holds the skin cells (bricks) together, helping to maintain the barrier's integrity and prevent moisture loss.
Ceramide-containing sunscreens not only protect against UV damage but also replenish these crucial lipids, strengthening the skin barrier and improving its ability to retain moisture. The National Eczema Association recognizes the importance of ceramides for skin barrier health.
What Does SPF Mean, and What Level of Protection Do I Need?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. It measures a sunscreen's ability to protect against UVB rays. The FDA recommends using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher.
However, for optimal protection, especially if you have sensitive skin or are spending extended time outdoors, an SPF of 30 or higher is recommended. Remember, no sunscreen blocks 100% of UV rays, so reapplication is essential.
How Much Sunscreen Should I Apply, and How Often?
Most people don't apply enough sunscreen. You should use about one ounce (a shot glass full) to cover your entire body, and a nickel-sized dollop for your face. Apply it liberally 15-30 minutes before sun exposure to allow it to absorb properly. Reapply every two hours, or immediately after swimming or sweating.
What's the Difference Between Chemical Sunscreens and Physical Sunscreens?
Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, which is then released from the skin. Common chemical filters include oxybenzone, avobenzone, octisalate, octocrylene, homosalate, and octinoxate.
Physical sunscreens, also known as mineral sunscreens, contain ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide that sit on top of the skin and physically block or reflect UV rays. Physical sunscreens are often preferred for sensitive skin.
Can Sunscreen Prevent Premature Aging and Wrinkles?
Absolutely! UV radiation is a major contributor to premature aging, causing wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, and loss of skin elasticity. Daily use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen is one of the most effective ways to prevent these signs of aging and maintain a youthful complexion. Studies have shown that regular sunscreen use can reduce the signs of photoaging by up to 24%.
How Does Sunscreen Affect Vitamin D Production?
While sunscreen can reduce vitamin D synthesis in the skin, most people can still get enough vitamin D through incidental sun exposure and diet. If you're concerned about vitamin D deficiency, talk to your doctor about getting your levels checked and consider taking a supplement.
Can Sunscreen Cause Acne or Breakouts?
Some sunscreens, particularly those with heavy, oily formulations, can clog pores and contribute to acne in acne-prone skin. However, there are many non-comedogenic (won't clog pores) and oil-free sunscreens available that are specifically designed for acne-prone or oily skin. Look for lightweight, gel-based formulas or those labeled "non-comedogenic."
Are There Any Environmental Concerns Associated with Sunscreen?
Certain chemical sunscreen ingredients, such as oxybenzone and octinoxate, have been shown to harm coral reefs. Some regions, like Hawaii, have banned the sale of sunscreens containing these ingredients. To minimize environmental impact, choose reef-safe sunscreens that contain mineral filters like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
Further Resources
- Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology: Changes in skin barrier function following the use of ceramide-containing sunscreen
- PR Newswire: New Research Reveals the Impact of UV Exposure on the Skin Barrier & the Benefits of Ceramides
- PubMed: Changes in skin barrier function following the use of ceramide-containing sunscreen




